RECOGNIZE QUALITY FROM THE METHOD
The choice of cutting-edge working methods allows us to optimize development times and start building a project's success right from the start. For this reason we pay particular attention to the usero oriented design and analysis (Human Centered Design, HCD) in all project phases in order to achieve high levels of UX / UI.
HARDWARE AND DESIGN
The process of designing hardware components for an IOT system involves the following development phases:
PHASE 1 - CUSTOMER NEEDS ANALYSIS
In phase 1, high-level and expensive acquisition sensors are used to identify the quantities of interest. Ex. National Instruments (NI) acquisition systems.
PHASE 2 - HW SPECIFICATIONS FOR FINAL ACQUISITION SYSTEM
Definition of the Cost Effective specifications of the final acquisition system. The system must be manageable and serviceable by the customer.
PHASE 3 - HW CUSTOMIZATION AND ALGORITHMS
- Control of physical dimensions.
- On-site data pre-processing.
- Aggregated data.
PHASE 4 - FW DEVELOPMENT
The algorithms for data pre-processing are transcribed at the FW level on microcontroller.
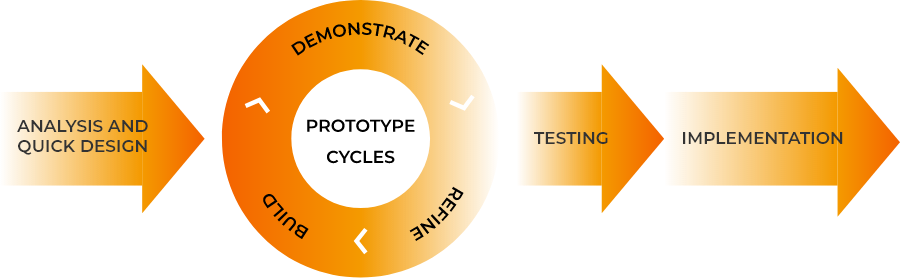
RAD - Rapid Application Developement
The SDLC methodology applied by MOKO is RAD, Rapid Application Developement. Essentially, RAD is the "test before buying" approach applied to software development.
RAD-based development cycles result in a lower level of rejection of the application when it is put into production.
The end user can work directly with the final formats as if it were in production: this leaves little space for the imagination and many errors are captured using this process.
To avoid looping request <-> responses, the development team does not use a pure RAD approach but rather harmonizes limited use of prototypes in project and project development.
Developed prototypes are specifically focused on one part of the application and do not provide a comprehensive integrated interface.

Human Centered Design - HCD
Particular attention is given to Human Centered Design (HCD) in all phases of the project in order to reach high UI / UX levels.